Application notes
Length and diameter determination of rod-like particles using Depolarized Dynamic Light Scattering (DDLS)
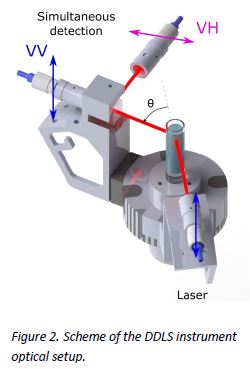
Anisotropic nanoparticles (NP) ,such as nanorods, nanotubes, nanodiscs etc. are widely used in such fields as medicine (fluorescent enhancers, tumor markers and light receptors), electronics (molecular electronic devices, sources of local heating) and many others. Self-assemblies of these NPs are also used for fabrication of advanced materials in which shape and size such as proteins or polymers of anisotropic NPs highly affect their properties and, as a result, have an influence on their efficiency in the final application.
Molecular weight measurement using Dynamic light Scattering equipment
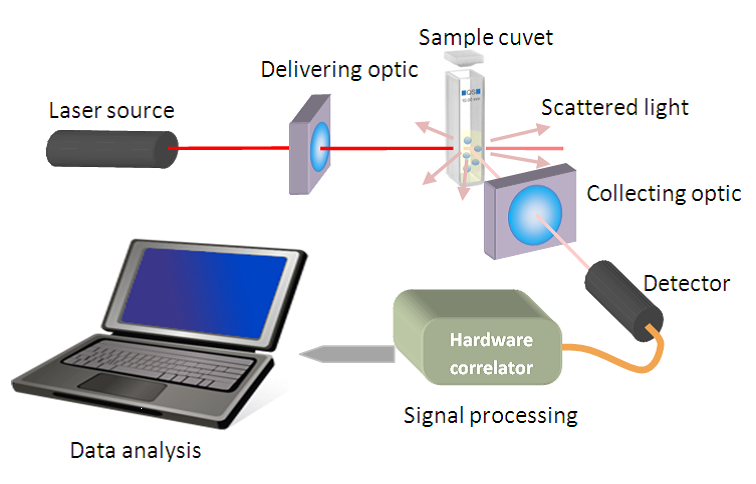
Aboslute molecualr weight (Mw) measurement is of primary importance for anyone that deals with macromolecules dispersed pigments such as proteins or polymers . Indeed molecular weight determines many important physical properties of matter like stifness, strength, viscosity, transition temperature from liquids to gels, etc. Today, there are many known ways to estimate or determine average molecular weight such as liquid chromatography, mass sperctrometry, ultra centrifugation, and in particular optical methods such as Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) and Static Light Scattering (SLS).
Ink pigment size characterization by Dynamic Light Scattering with the VASCOTM analyzer
Printing inks made of nano sized pigments dispersed in liquids are more than ever used in the industry because of their unique properties. Characterizing the size of the dispersed pigments at initial concentration in such inks is often mandatory in order to guaranty stability and adequate physical/chemical properties. Unfortunately, such characterization remains an inaccessible challenge to most conventional optical measurement techniques like Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) systems because of high concentrations effects. But such limitations are note a fate; thus in this note, we demonstrate through some illustrative examples how the VASCOTM analyzer, thanks to its unique innovative patented optical cell design, can overcome these limitations for the characterizations of dark/colored and concentrated colloidal suspensions. A concrete example of industrial application is presented with the measurement of concentrated pigmented jet printer inks.
Pharmaceutics
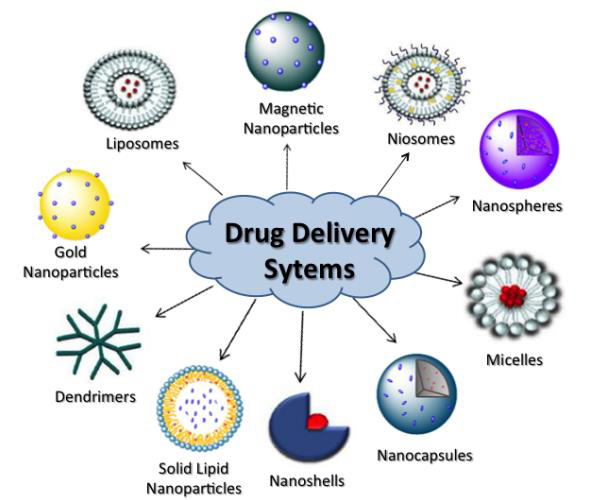
Pharmaceutics is the science of preparing and dispersing of active pharmaceutical ingredients (also abbreviated as API) their delivery to the target and a formulation of final medicament. In order to deliver APIs to their target in living organism, scientists use biocompatible polymers, proteins, drug encapsulation into polymeric shell or into liposome, nanoparticles and many other systems.
Monitoring protein aggregation in injectable vaccines syringes: a new direct & contactless technique
Aggregation of proteins and active principle ingredients (API) in injectable biopharmaceutical products remains a major concern impacting the stability and usability of a product. This mechanism is still not well understood. The Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) in situ monitoring of the denaturation and degradation process of therapeutic proteins during production and storage can be a key competitive advantage for manufacturers and researchers.
NIR Dynamic Light Scattering for Quantum Dots Size Measurement
Since QD size (usually,≤30 nm) is the key to their optical properties, Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) presents itself as an interesting candidate for such characterization, since it enables a representative size measurement of small nanoparticles (NPs) in suspensions. To avoid the difficulties due the QDs absorption properties, replacement of the classical 635-nanometers laser by a near-infrared (NIR) 780-nanometers laser in the DLS apparatus made such a measurement possible. This study makes evidence that it is possible to extend the range of DLS uses for fluorescent particles with strong absorbance in the visible, making it a promising characterization technique for fluorophore-based system, especially in the biomedical field.