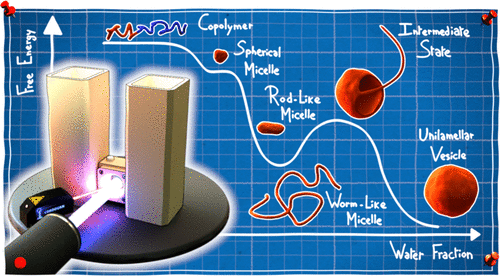
Solution self-assembly of amphiphilic block copolymers (BCs) is typically performed by a solvent-to-water exchange. However, BC assemblies are often trapped in metastable states depending on the mixing conditions such as the magnitude and rate of water addition. BC self-assembly can be performed under near thermodynamic control by dialysis, which accounts for a slow and gradual water addition. (340 characters)